In the digital era, 3D modelling and texturing are crucial in entertainment, media, healthcare, and education. These approaches are changing how we make and see items and fostering innovation and creativity. Open Verse VFX Academy offers comprehensive 3D modelling and texturing training to help you stay competitive. This blog discusses 3D modelling and texturing, their uses, process, techniques, and how to learn them
What is 3D modelling/texturing?
3D modelling creates a three-dimensional image of an object or surface. Using specialised software, artists and designers may edit virtual vertices to construct a mesh. These meshes may be polished into complicated creations.
However, texturing gives the 3D object colour, detail, and realism by adding pictures or patterns. Textures may resemble wood, metal, cloth, and skin, giving 3D objects depth and realism. Modelling and texturing make digital objects appear genuine.
Why is 3D modelling and texturing used?
Media and entertainment
The entertainment and media sector uses 3D modelling and texturing extensively. 3D models are essential for immersive content in blockbusters, animated films, video games, and virtual reality. Modelling and texturing characters, locations, special effects, and objects creates magnificent scenarios that capture spectators.
Product Design and Manufacturing
3D modelling lets designers build precise prototypes of items before they are manufactured. This helps visualise the final product, find design issues, and make improvements. Marketing materials using 3D models provide potential clients a realistic image of the goods.
Architecture, Real Estate
Architects and real estate experts utilise 3D modelling to visualise structures and interiors. This shows clients a realistic project before construction. Clients may make educated selections and architects can convey their ideas using 3D models of architectural designs, interior layouts, and landscape.
Virtual and Augmented Reality
VR and AR use 3D modelling and texturing to create immersive experiences. Users can engage with a wholly digital environment in VR, whereas AR adds digital components to reality. Users need high-quality 3D models for a smooth and realistic experience in both apps.
Medical and Healthcare
Medical and healthcare professionals utilise 3D modelling to create accurate human anatomy models for teaching, surgery planning, and simulation. 3D models assist doctors visualise complicated structures and procedures, boosting therapy accuracy and efficacy.
Training and Education
Education and training benefit from 3D modelling. From interactive science simulations to historical recreations, 3D models make complicated subjects easier to understand. Students can engage and connect with subjects better using them.
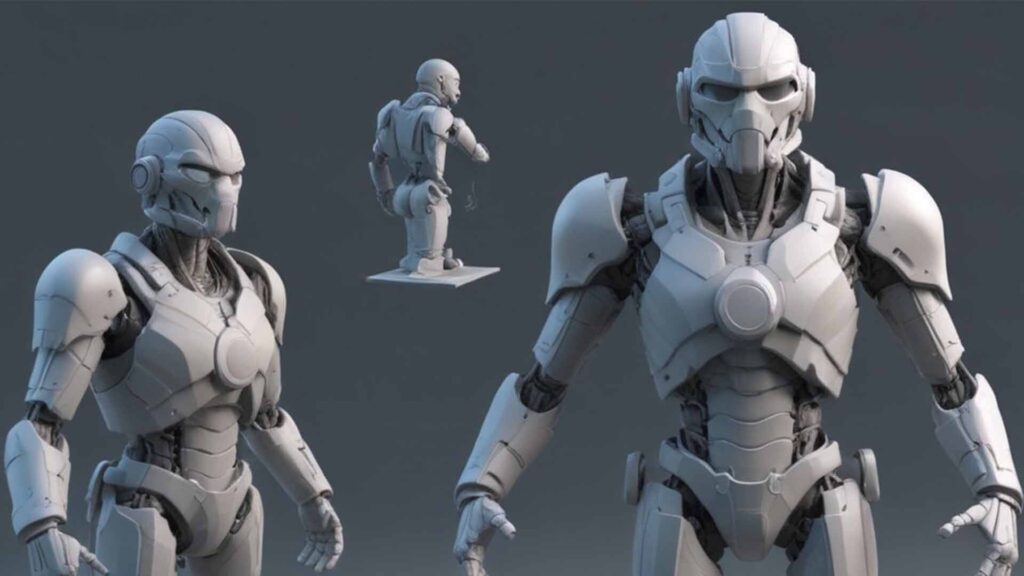

Overview of 3D Modelling
Each stage of 3D modelling is essential to producing a high-quality output. Summary of usual workflow:
Conceptualization
First, ideas are brainstormed and drawings or plans are made. Understanding project requirements, scope, and design is done at this stage.
Modelling
The modelling process begins when the notion is understood. Artists manipulate vertices, edges, and faces in 3D modelling software to form the object’s shape. This step creates model geometry and structure.
Texturing
After modelling, texturing begins. Artists add texture to 3D models for colour, detail, and material qualities. UV maps are used to unwrap the 3D model onto a 2D surface for correct texture application.
Rigging, Animation
Animating a 3D object requires rigging. Create a rig to move and pose the model. Animation then gives the model life by specifying its motions and behaviours.
Rendering
In the last stage, the 3D scene is rendered into pictures or animations. Lighting, cameras, and other environmental conditions are set up to create visual effects.
After Production
Post-production may be needed for cartoons and films. This involves editing, compositing, and adding additional effects to improve the final product.

Most Common 3D Modelling Methods
Polygonal modelling
Polygonal modelling—usually triangles and quads—is the most prevalent method. Creating elaborate and complicated models with this flexible approach is popular.
NURBS modelling
Smooth surfaces are created using NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) modelling using mathematical curves. Automotive and industrial designers utilise this method to create complicated designs.
Sculpting
Sculpting includes moulding a digital model like clay. Artists may push, tug, and smooth the surface to create organic, intricate shapes. This method is utilised for character modelling and complex detailing.
Procedural modelling
Procedure modelling generates models automatically using algorithms and rules. Complex landscapes, cities, and flora may be created with this method.

Learning 3D Modelling
Take a 3D Modelling Course
A organised training is one of the finest methods to learn 3D modelling. Open Verse VFX Academy teaches 3D modelling and texturing from beginner to expert. Our courses give you hands-on experience and practical information to establish a solid 3D modelling foundation.
Practice Often
It takes practice to perfect 3D modelling. Work on own projects, replicate models, and try new methods. Practice improves skill.
Employ Online Resources
There are many online courses, forums, and community organisations for 3D modelling. Artists provide instructions and advice on YouTube, Blender Guru, and CG Cookie.
Community Join
3D artist communities offer support, critique, and inspiration. Attend classes, join online forums, and work with other artists to grow and remain inspired.
Most Popular 3D Modelling Software
AutoCAD Maya
One of the most popular 3D modelling applications is Autodesk Maya. Professionals in cinema, animation, and game development love it for its modelling, texturing, rigging, and animation tools.
The Blender
Hobbyists and professionals utilise Blender, a sophisticated, open-source 3D modelling programme. It has many features, high flexibility, and strong community support.
3ds Max
Another popular Autodesk product, 3ds Max, has powerful modelling and rendering capabilities. Architectural visualisation, product design, and game development use it extensively.
The ZBrush
ZBrush is specifically for digital sculpting and painting. Character painters and designers love it for producing intricate models.
Cinema 4D
Cinema 4D has a simple interface and strong modelling, animation, and rendering features. Motion graphics, visual effects, and animation use it extensively.
Houdini
Houdini is a powerful procedural modelling and visual effects programme. The film and game industries utilise it to create intricate simulations and effects.
Conclusion
Today’s digital world requires 3D modelling and texturing talents in many businesses. Mastering these abilities can open doors in entertainment, product design, architecture, and virtual reality. Open Verse VFX Academy offers comprehensive 3D modelling and texturing courses to help you start and succeed in this fascinating sector. You may realise your creative ambitions and create an impact in 3D art with the correct tools, skills, and devotion.
Start 3D modelling today with Open Verse VFX Academy and discover new possibilities!